What is Virtual Design and Construction (VDC)? The Ultimate Guide
Discover the real VDC meaning and how Virtual Design and Construction is transforming project planning, collaboration, and efficiency in the modern construction industry.
In today’s fast-paced construction industry, delivering projects on time and within budget requires more than just blueprints and spreadsheets. It demands integration, precision, and foresight. That’s where Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) comes in — a process that’s transforming how buildings are planned, built, and managed.
While many people associate VDC with Building Information Modeling (BIM), they’re not quite the same. Let’s dive into what VDC means, how it compares to BIM, and why it’s becoming a cornerstone of modern construction.
Defining Virtual Design and Construction (VDC)
Virtual Design and Construction (VDC) is a management methodology that uses digital tools to create multidisciplinary performance models of a project’s product (the building or infrastructure), processes, and organization. Pioneered in 2001 by Stanford University’s Center for Integrated Facility Engineering (CIFE), VDC allows teams to build a project virtually before breaking ground in the real world. Think of it as creating a “digital twin” that simulates every aspect of a project, from design to delivery.
VDC comprises several core components:
- Building Information Modeling (BIM): Data-rich 3D models that represent a project’s physical and functional characteristics.
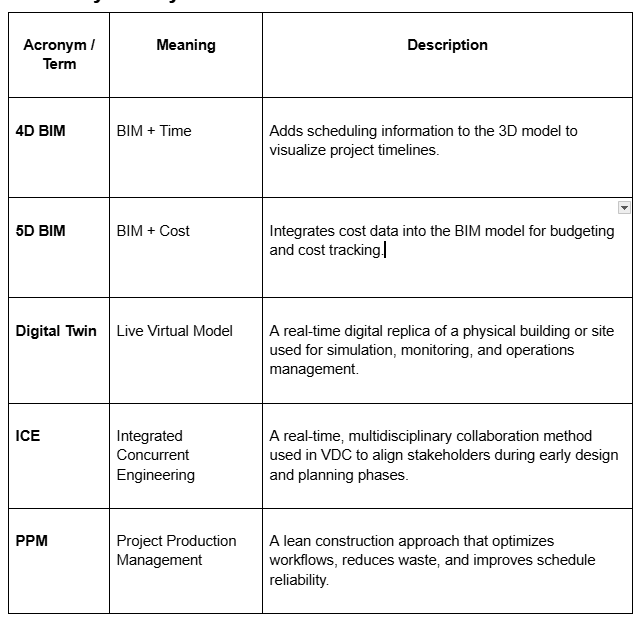
- Integrated Concurrent Engineering (ICE): Real-time collaboration sessions where architects, engineers, and contractors align on design and planning.
- Project Production Management (PPM): Lean construction principles to optimize workflows, schedules, and resources.
- Metrics: Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) to track progress and ensure alignment with project goals.
Unlike traditional approaches, VDC goes beyond design to encompass planning, cost estimation, scheduling, and risk management, making it a holistic strategy for project success.
Understanding BIM and Its Role in VDC
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is often confused with VDC, but it’s just one piece of the puzzle. BIM is a process for creating and managing 3D models packed with data about a project’s components—think walls, HVAC systems, or plumbing, all detailed down to their materials and costs. These models serve as a digital foundation for VDC, enabling collaboration and precision.
BIM supports VDC by:
- Centralizing Data: Architects, engineers, contractors, and owners work from a single source of truth, reducing miscommunication.
- Clash Detection: Identifying conflicts (e.g., a pipe running through a beam) before construction begins.
- Enhanced Visualization: Allowing stakeholders to “walk through” a virtual building to refine designs — often through a 3D virtual tour experience that improves spatial understanding and design validation.
The key difference? BIM focuses on modeling and data management, while VDC integrates BIM with people, processes, and project management. To use an analogy: BIM is the detailed blueprint, while VDC is the entire strategy for turning that blueprint into a finished building. While VDC often relies on BIM, it can also function without it, incorporating other tools or methods for project optimization.
Benefits of VDC in the AEC Industry
VDC is a game-changer for construction projects, offering benefits that save time, money, and resources.
Enhanced Collaboration
VDC breaks down silos by fostering real-time communication. Through cloud-based platforms and ICE meetings, teams collaborate seamlessly, catching issues early.
Improved Efficiency and Cost Savings
Rework—fixing mistakes during construction—can account for up to 30% of project costs. VDC minimizes this by using clash detection and simulations to identify problems in the virtual stage, streamlining workflows.
Better Visualization and Planning
VDC’s digital twins, combined with 4D (time) and 5D (cost) modeling, let teams visualize and optimize every phase of a project. This ensures schedules stay on track and budgets remain under control.
Sustainability and Safety
VDC supports sustainable practices, like adaptive reuse to reduce embodied carbon, and enhances safety by simulating hazardous scenarios virtually. Teams can plan safer workflows before workers step onto the site.
Increased Productivity
By aligning with lean construction principles, VDC reduces waste and boosts efficiency, ensuring resources are used effectively and deadlines are met.
How Realsee Enhances VDC Workflows
When implementing Virtual Design & Construction (VDC), real-world accuracy and real-time communication are crucial. Realsee offers a suite of 3D capture tools and AI-powered virtual tour software that seamlessly bridge the gap between digital models and physical construction sites:
- High-precision 3D LiDAR Camera capture with devices like the Galois M2, enabling Realsee to recreate indoor and outdoor spaces at 134 MP resolution with millimeter-level accuracy. This supports alignment of field conditions with BIM models for clash detection, field verification, and digital twin updates.
- Effortless capture using smartphones or 360° cameras powered by Realsee’s monocular vision AI algorithm, simplifying site scanning without specialized hardware — democratizing model creation across project teams.
- With just one scan, Realsee delivers accurate floor plans, point clouds, panoramas, and 3D models — all instantly accessible in the cloud. VDC teams can view the latest site data anytime, from anywhere, helping them validate schedules, spot construction risks early, and stay aligned on cost decisions.
- Interactive collaboration tools, including white-label branding, embedded multimedia, and live 3D calls, which facilitate Integrated Concurrent Engineering (ICE) sessions and remote stakeholder walkthroughs—enhancing communication and reducing on-site errors.
By integrating Realsee’s 3D capture and virtual tour ecosystem, VDC practitioners gain:
- Accurate as-built verification comparing virtual and actual site conditions.
- Improved decision-making through real-time, immersive walkthroughs and point-cloud visualizations.
- Enhanced team coordination with remote access for contractors, owners, and engineers — made even more effective through immersive virtual tour capabilities that allow real-time walkthroughs from anywhere.
- Reduced rework and miscommunication through data transparency and collaborative tools.
Glossary of Key Terms
Finally
Virtual Design & Construction is more than a buzzword—it represents a paradigm shift in construction. It takes BIM beyond drawing rooms and integrates it into real-world execution, driving coordination, cost savings, and predictability.
For construction leaders pursuing efficiency and quality, VDC is now essential, not optional. The future of AEC lies in digital twins, live data flows, and proactive workflows—and those who adopt VDC today are building smarter, faster, and more sustainably.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between BIM and VDC?
BIM (Building Information Modeling) is the process of creating and managing data-rich 3D models of buildings or infrastructure. It focuses on the digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a structure. VDC (Virtual Design and Construction) goes beyond that — it integrates BIM with people, workflows, schedules, cost management, and collaboration strategies to optimize the entire construction lifecycle.
In short, BIM is the tool; VDC is the method that brings it all together.
2. What do VDC engineers do?
They use digital tools to plan and coordinate construction projects.That includes managing BIM models, running clash checks, syncing schedules and budgets, and making sure teams work together smoothly.
3. What is the VDC process?
The VDC process typically includes the following phases:
- Modeling – Using BIM tools to digitally represent the structure.
- Integration – Bringing in scheduling (4D), cost (5D), and field data for full project context.
- Collaboration – Conducting real-time ICE sessions with all stakeholders.
- Validation – Running simulations and clash detection to catch issues early.
- Execution & Handover – Using updated models to guide construction, and eventually supporting facility management via digital twins.
Each step is designed to improve accuracy, reduce waste, and keep the project on time and on budget.